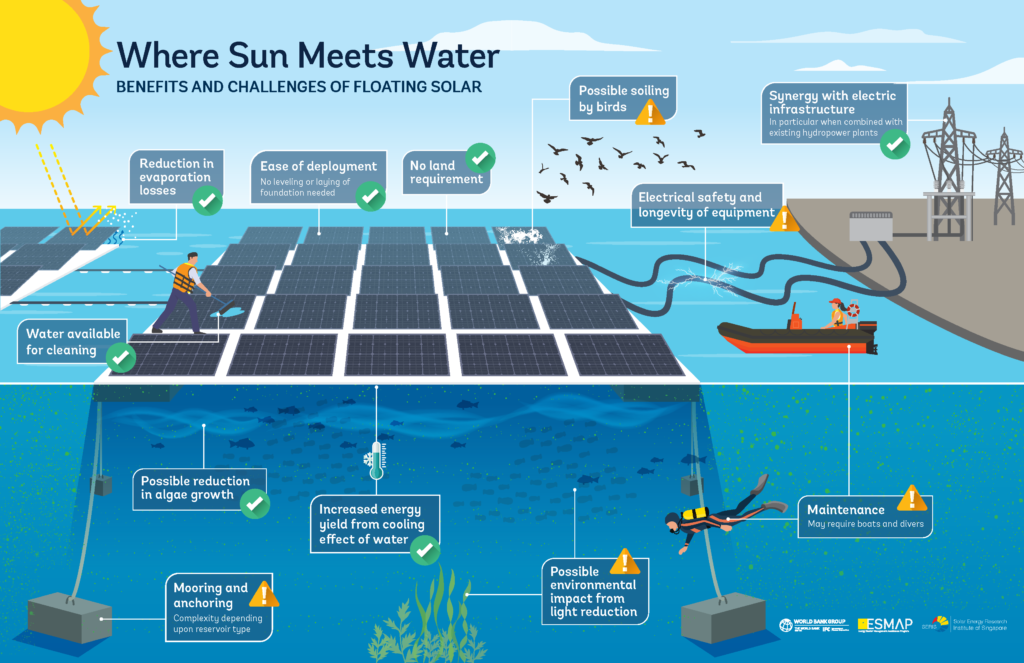
Falling development costs combined with limited land availability in densely populated countries have seen floating PV (FPV) pitched as the third pillar of the solar sector alongside ground-mounted and rooftop installations.
Basically, the water bodies are covered with photovoltaic modules thanks to a floating structure. The floating solar is the combination of floats and solar panels, the whole system is anchored on the bottom, on the banks or with hybrid systems.
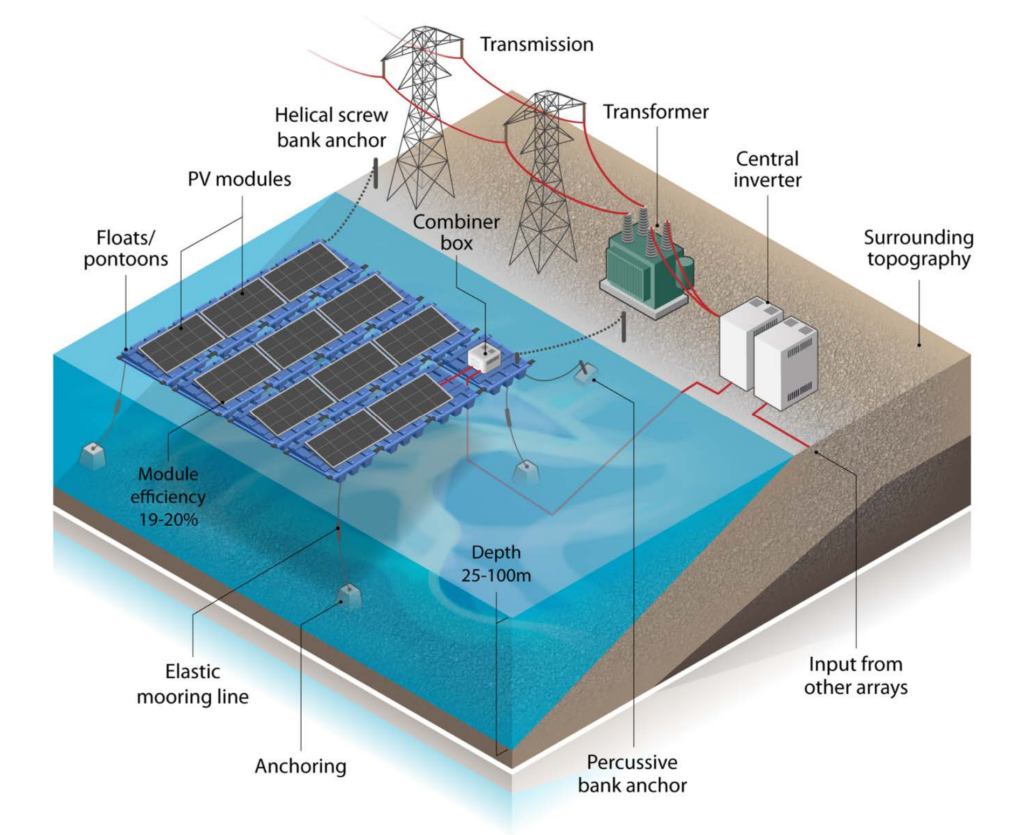
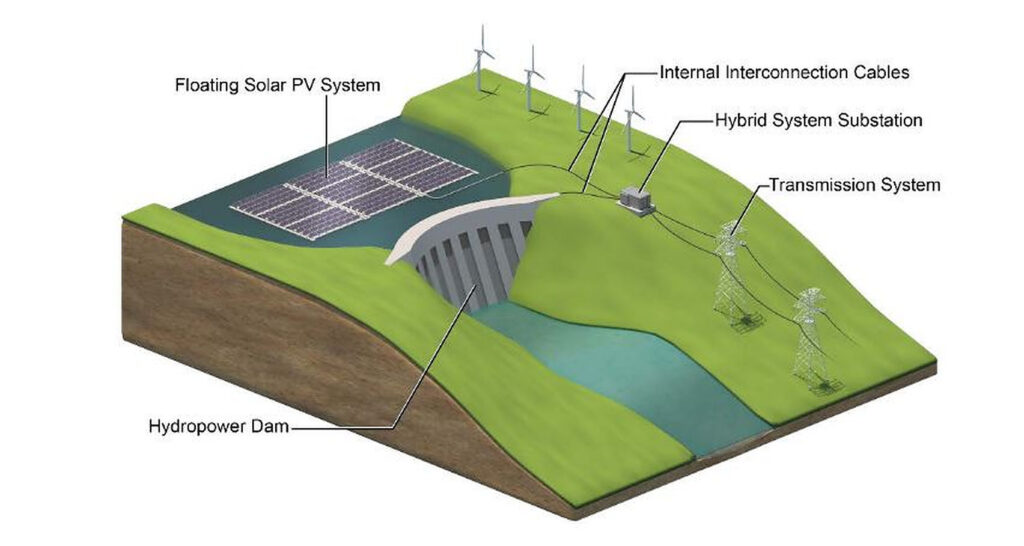
The great advantage of floating solar is to allow the production of renewable energy where the earth is scarce, as well as to allow the production of energy in tandem with other sources, such as hydroelectricity.
Floating solar systems can be used by companies, industries, public institutions or local authorities. They can meet the clean energy needs on site or feed electricity into the grid.